Load Unit Physics . Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. What is load, and what is its unit? Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration of the earth (9.8 m/sec2), and the height in meters. The fulcrum is the point on which the. The effort (input force) and load (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the difference? The load is the object that is moved or lifted. In physics, the term load is used to talk about objects being lifted or moved by machines. The fulcrum is the pivot point, and the effort is the force required to lift or move. This educational exploration breaks down the concept of loads, helping young minds.
from www.dreamstime.com
What is load, and what is its unit? The effort (input force) and load (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. In physics, the term load is used to talk about objects being lifted or moved by machines. This educational exploration breaks down the concept of loads, helping young minds. The fulcrum is the pivot point, and the effort is the force required to lift or move. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. The fulcrum is the point on which the. We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the difference? Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration of the earth (9.8 m/sec2), and the height in meters. Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body.
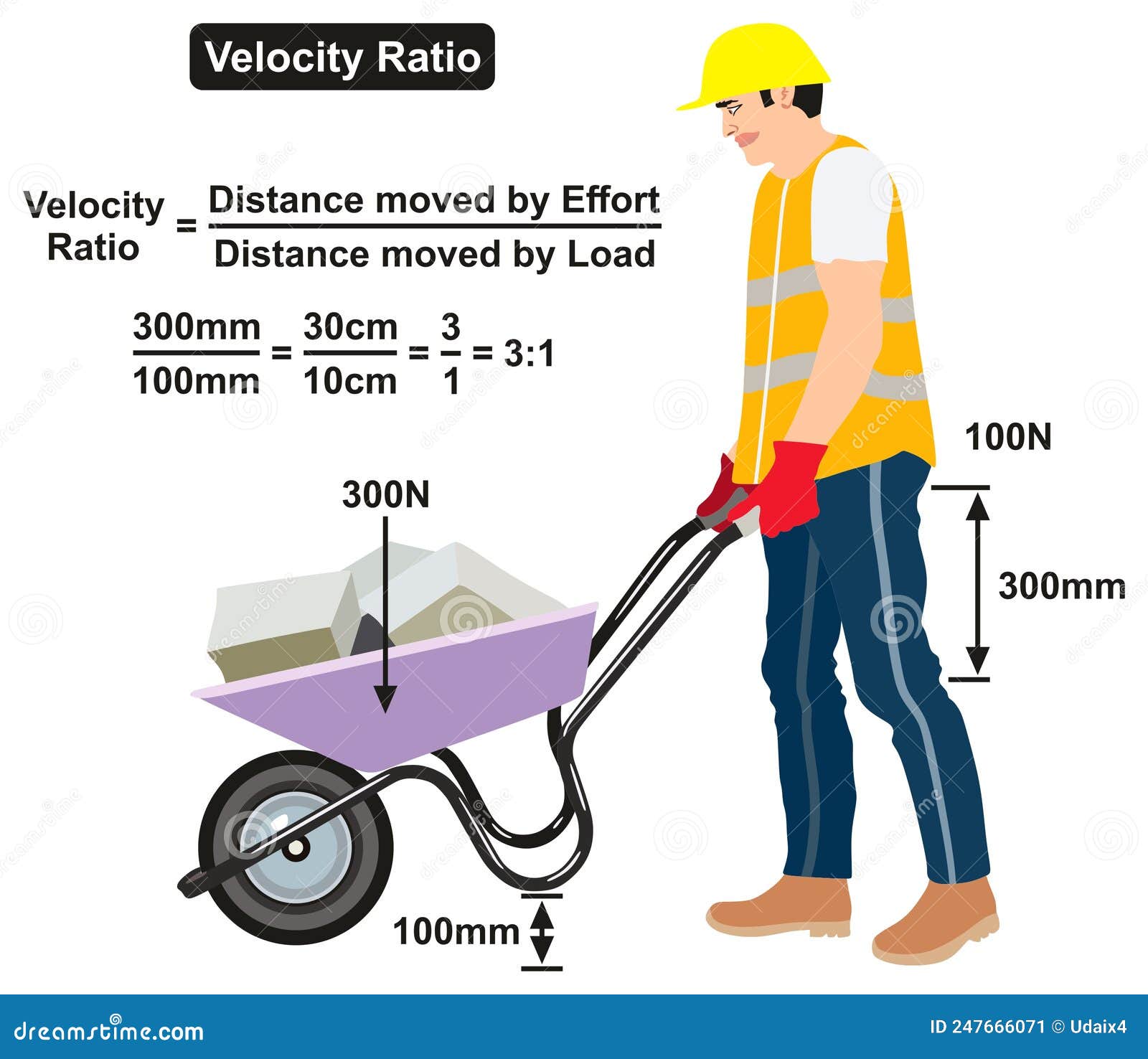
Velocity Ratio Infographic Diagram Example of Man Push Effort
Load Unit Physics Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration of the earth (9.8 m/sec2), and the height in meters. The effort (input force) and load (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. In physics, the term load is used to talk about objects being lifted or moved by machines. The fulcrum is the point on which the. Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. The fulcrum is the pivot point, and the effort is the force required to lift or move. This educational exploration breaks down the concept of loads, helping young minds. What is load, and what is its unit? Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration of the earth (9.8 m/sec2), and the height in meters. We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the difference?
From physics.stackexchange.com
newtonian mechanics Vertical Load Reactions On A Ramp Physics Stack Load Unit Physics The load is the object that is moved or lifted. We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the difference? This educational exploration breaks down the concept of loads, helping young minds. The fulcrum is the pivot point, and the effort is the force required to lift or move. The effort (input force) and load. Load Unit Physics.
From localrevive.com
What Is It? How Does It Work? Types & Process (2022) Load Unit Physics We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the difference? Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration of the earth (9.8 m/sec2), and the height in meters. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a. Load Unit Physics.
From petervaldivia.com
Electricity. The movement of the electron Load Unit Physics What is load, and what is its unit? Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. The fulcrum is the point on which the. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the difference? This. Load Unit Physics.
From www.youtube.com
Unit load method (easiest way) for all types of structures YouTube Load Unit Physics The fulcrum is the point on which the. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. In physics, the term load is used to talk about objects being lifted or moved by machines. Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. What is load, and what is its. Load Unit Physics.
From sinevaledoaco.blogspot.com
Material Handling Equipment Unit Load Load Unit Physics Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration of the earth (9.8 m/sec2), and the height in meters. The fulcrum is the point on which the. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. In physics, the term load is used to talk about objects being lifted or moved by machines. We use these words on. Load Unit Physics.
From www.chegg.com
The Distributed Load In Figure 7 Varies Linearly F... Load Unit Physics The fulcrum is the pivot point, and the effort is the force required to lift or move. Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. This educational exploration breaks down the concept of loads, helping young minds. What is load,. Load Unit Physics.
From www.slideshare.net
Physics Units & Definitions Load Unit Physics This educational exploration breaks down the concept of loads, helping young minds. In physics, the term load is used to talk about objects being lifted or moved by machines. We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the difference? The fulcrum is the point on which the. What is load, and what is its unit?. Load Unit Physics.
From www.pandhengineering.co.uk
Pipe sizing The CIPHE loading units method P&H Engineering Load Unit Physics This educational exploration breaks down the concept of loads, helping young minds. The fulcrum is the pivot point, and the effort is the force required to lift or move. What is load, and what is its unit? Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. We use these words on. Load Unit Physics.
From www.pandhengineering.co.uk
Pipe sizing The CIPHE loading units method P&H Engineering Load Unit Physics Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. The fulcrum is the pivot point, and the effort is the force required to lift or move. What is load, and what is its unit? The fulcrum is the point on which. Load Unit Physics.
From www.youtube.com
Unit load method 1 YouTube Load Unit Physics The fulcrum is the pivot point, and the effort is the force required to lift or move. What is load, and what is its unit? This educational exploration breaks down the concept of loads, helping young minds. Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration of the earth (9.8 m/sec2), and the height in meters. Load is a. Load Unit Physics.
From engineersfield.com
Properties of materials, measurement of physical quantities like length Load Unit Physics Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. This educational exploration breaks down the concept of loads, helping young minds. What is load, and what is its unit? The fulcrum is the point on which the. Multiply the mass of. Load Unit Physics.
From www.slideshare.net
Physics form 4 chapter 2 Load Unit Physics Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the difference? The effort (input force) and load (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. Multiply. Load Unit Physics.
From sparkypedia.electricianu.com
Dwelling Unit Service Load Calculations Optional Method Sparkypedia Load Unit Physics The fulcrum is the point on which the. What is load, and what is its unit? Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration of the earth (9.8 m/sec2), and the height in meters. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the. Load Unit Physics.
From www.youtube.com
SYSTEM OF UNITS YouTube Load Unit Physics Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. The fulcrum is the pivot point, and the effort is the force required to lift or move. Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration of the earth (9.8 m/sec2), and the height in meters. In physics, the term load. Load Unit Physics.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Introduction and Building Loads PowerPoint Presentation, free Load Unit Physics The load is the object that is moved or lifted. The effort (input force) and load (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. The fulcrum is the pivot point, and the effort is the force required to lift or move. We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the difference? Load is. Load Unit Physics.
From sinevaledoaco.blogspot.com
Material Handling Equipment Unit Load Load Unit Physics The fulcrum is the point on which the. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. We use these words on a daily basis, but do you really know the difference? The effort (input force) and load (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. What is load, and what is its unit? Multiply the mass. Load Unit Physics.
From www.structuralbasics.com
Live load all you need to know Load Unit Physics In physics, the term load is used to talk about objects being lifted or moved by machines. Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration of the earth (9.8 m/sec2), and the height in meters. This educational exploration breaks down the concept of loads, helping young minds. The fulcrum is the point on which the. Load is a. Load Unit Physics.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Structural analysis unit load method Studypool Load Unit Physics Load is a term frequently used in engineering to mean the force exerted on a surface or body. The load is the object that is moved or lifted. What is load, and what is its unit? The effort (input force) and load (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. Multiply the mass of the object by the. Load Unit Physics.